fasting for weight loss
In fact, it has been a part of human history for centuries, practiced for religious, spiritual, and healthrelated reasons. From the ancient Greeks to modernday cultures, we have long understood the profound impact of fasting on the human body. However, it is only in recent decades that we have begun to unravel the intricate scientific mechanisms that make fasting a powerful tool for weight management and overall health improvement.
The Metabolic Switch: From Glycogen to Fat Burning
At the heart of fasting's effectiveness for weight loss is a fundamental metabolic shift. When we consume food, especially carbohydrates, our bodies produce insulin to help shuttle glucose from the bloodstream into our cells for energy. This process is highly efficient, and our bodies prefer to use glucose as their primary fuel source. Excess glucose is stored as glycogen in our liver and muscles.
When we fast, we deplete these glycogen stores. Typically, this takes anywhere from 12 to 24 hours, depending on individual metabolism and physical activity. Once the glycogen reserves are exhausted, our bodies have no choice but to tap into their secondary fuel source: stored body fat. The liver begins to convert fatty acids into ketone bodies, which are then used as fuel by the brain and other organs. This metabolic state, known as ketosis, is where the magic of fat loss truly happens. We are, in essence, training our bodies to become "fatadapted," utilizing our own fat reserves for energy rather than relying on a constant intake of food.
Hormonal Regulation: The Key to Sustained Fat Loss
Fasting is not just about calorie restriction; it is a powerful hormonal regulator. We have observed that periods of fasting lead to significant changes in several key hormones that influence appetite, metabolism, and fat storage.
Insulin: As mentioned, fasting dramatically lowers insulin levels. High insulin levels are a major driver of fat storage and can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes. By keeping insulin low, we create an environment where the body can more easily access and burn stored fat.
Human Growth Hormone (HGH): Fasting has been shown to cause a substantial increase in the production of HGH. This hormone is crucial for muscle repair, growth, and the maintenance of lean body mass. The elevated levels of HGH during a fast help to protect muscle tissue from being broken down for energy, ensuring that the majority of weight loss comes from fat stores rather than muscle.
Norepinephrine (Adrenaline): Fasting stimulates the nervous system, leading to an increase in norepinephrine. This hormone is known to increase metabolic rate and promote the breakdown of fat cells, making the stored fat available for energy.
Ghrelin and Leptin: These are our hunger and satiety hormones, respectively. While fasting can initially increase ghrelin (the hunger hormone), many individuals report that after a certain period, their hunger levels actually decrease. This is often attributed to the body becoming more efficient at managing its energy and the stabilizing effect of ketosis.
Exploring Popular Fasting Methods for Weight Loss
The term "fasting" can be applied to a variety of approaches, each with its own set of rules and benefits. We have found that the most effective method is the one that an individual can consistently adhere to.
Intermittent Fasting (IF): The Foundation of Modern Fasting
Intermittent fasting is not a diet but an eating pattern that cycles between periods of eating and fasting. This approach is highly flexible and can be adapted to various lifestyles.
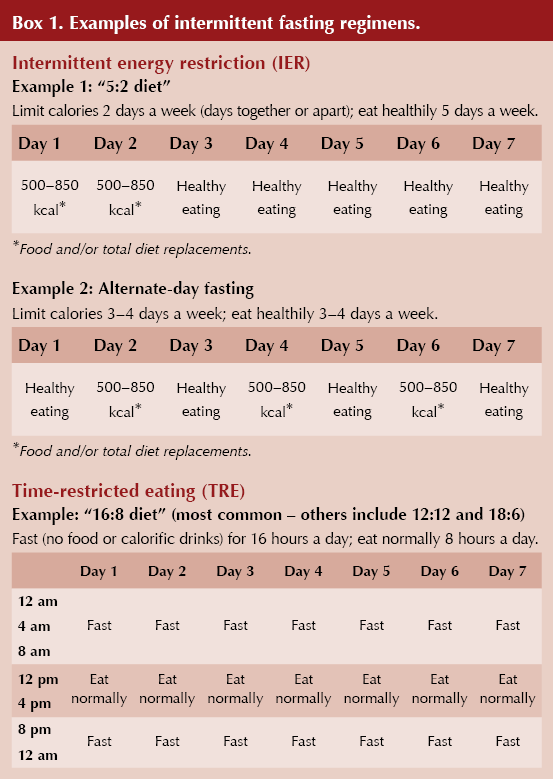
The 16/8 Method (Leangains Protocol): This is one of the most popular and easiesttofollow methods. It involves fasting for 16 hours and restricting your eating window to 8 hours. For example, if you finish dinner at 8 p.m., you would not eat again until noon the next day. This method is often recommended for beginners due to its simplicity and the fact that a significant portion of the fasting period is spent sleeping. We have observed that the 16/8 method is highly effective for improving insulin sensitivity and promoting fat loss.
The 5:2 Diet: This method involves eating normally for five days of the week and restricting calorie intake to 500600 calories on two nonconsecutive days. This approach allows for flexibility and can be less intimidating than daily fasting. We have seen that the 5:2 diet can be a great way to ease into a fasting lifestyle and achieve sustainable weight loss.
EatStopEat: This involves a full 24hour fast, once or twice per week. For example, you might fast from dinner on Monday until dinner on Tuesday. This method requires a higher level of discipline but can be highly effective for those who want a more aggressive approach to weight loss.
The Warrior Diet: Developed by Ori Hofmekler, this method involves a 20hour fast with a single, large meal consumed within a fourhour eating window at night. The focus during the fasting period is on consuming small amounts of raw vegetables and fruits. We have found that this method is often favored by those with very active lifestyles, as it aligns with the body's natural circadian rhythms.
Prolonged Fasting: Deeper Metabolic and Cellular Benefits
Prolonged fasting, typically defined as fasting for more than 24 hours, takes the metabolic benefits of intermittent fasting to a new level.
24Hour Fast: This is a simple yet powerful way to reset your metabolism. We have found that a 24hour fast can be a great way to break a weight loss plateau and improve insulin sensitivity.
36Hour to 72Hour Fast: These longer fasts are where the deeper metabolic changes begin to occur. We have observed that prolonged fasts can significantly increase autophagy (the body's process of cleaning out damaged cells), enhance ketosis, and provide a substantial metabolic boost. However, we strongly recommend that prolonged fasting be undertaken with caution and under medical supervision, especially for individuals with underlying health conditions.
Maximizing Your Results: The Synergy of Fasting and Diet
Fasting is a powerful tool, but it is not a magic bullet. To achieve lasting weight loss and optimal health, we must complement our fasting schedule with a nutrientdense, wholefoods diet during our eating windows.
What to Eat During Your Eating Window
Focus on Whole Foods: We recommend prioritizing foods that are minimally processed and rich in nutrients. This includes:
Lean Proteins: Chicken, fish, eggs, and legumes are essential for building and maintaining muscle mass.
Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil provide satiety and are crucial for brain health.
Complex Carbohydrates: Vegetables, fruits, and whole grains provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Avoid Processed Foods and Sugary Drinks: We have observed that consuming processed foods, refined sugars, and sugary drinks during the eating window can negate the positive effects of fasting. These foods spike insulin levels and can lead to cravings, making it harder to stick to the fasting schedule.
Hydration and Electrolytes: The Unsung Heroes of Fasting

Staying hydrated is absolutely critical during a fast. We recommend consuming plenty of water, as well as electrolyterich fluids like black coffee, herbal tea, and bone broth. Electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium are essential for nerve function and muscle contractions, and they can become depleted during a fast.
Addressing Common Concerns and Myths About Fasting
Fasting is often misunderstood, and many myths persist. We believe it is our responsibility to provide clear, evidencebased information to help individuals make informed decisions about their health.
Myth 1: Fasting Puts Your Body into "Starvation Mode"
This is one of the most persistent myths. The idea is that fasting slows down your metabolism to conserve energy. While this can happen with longterm, extreme calorie restriction, the shortterm nature of intermittent fasting and the hormonal changes it induces actually work to increase metabolic rate. We have observed that fasting helps the body become more efficient at using fat for fuel, which is the opposite of "starvation mode."
Myth 2: Fasting Leads to Muscle Loss
As we mentioned earlier, fasting leads to an increase in human growth hormone (HGH), which helps to protect muscle tissue. Additionally, when we are in a state of ketosis, our bodies prefer to use fat for fuel, sparing muscle glycogen. We have found that individuals who combine fasting with strength training are often able to maintain or even build muscle mass while losing fat.
Myth 3: Fasting Will Make You Tired and Moody
While some individuals may experience a period of adaptation, many people report increased energy and mental clarity after a few weeks of fasting. The brain thrives on ketones, and the steady energy supply from fat stores can lead to more stable energy levels throughout the day.
Fasting and Its Broader Health Benefits
While our primary focus here is weight loss, we must also acknowledge the broader health benefits that fasting can provide.
Cellular Repair and Autophagy
Autophagy, from the Greek for "selfeating," is the body's way of cleaning out old, damaged cells and recycling their components. This process is crucial for preventing disease and promoting longevity. We have seen that prolonged fasts, in particular, can significantly increase the rate of autophagy, leading to a profound cellular rejuvenation.
Brain Health and Cognitive Function

The production of ketones during a fast provides a highly efficient fuel source for the brain. We have observed that this can lead to improved cognitive function, enhanced mental clarity, and a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
Improved Insulin Sensitivity and Blood Sugar Control

As discussed, fasting is one of the most effective ways to improve insulin sensitivity. This is crucial for preventing and managing type 2 diabetes. We have seen firsthand how fasting can help individuals regain control over their blood sugar levels.
Reduced Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a silent killer, linked to a host of diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. Fasting has been shown to reduce markers of inflammation in the body. We believe this is one of the most significant longterm benefits of a fasting lifestyle.
Our Recommendations for Starting Your Fasting Journey
If you are new to fasting, we recommend starting slowly and listening to your body.
Start with a Simple Method: We suggest beginning with the 16/8 method. It is a gentle way to introduce your body to fasting and see how you feel.
Stay Hydrated: This is nonnegotiable. Always have water, black coffee, or herbal tea on hand.
Prioritize NutrientDense Foods: During your eating window, focus on quality over quantity.

Listen to Your Body: If you feel unwell, break your fast. Fasting should not be a source of stress or discomfort.
Consult a Healthcare Professional: If you have any underlying health conditions, such as diabetes, a history of eating disorders, or are pregnant or breastfeeding, we strongly advise you to consult with a doctor or registered dietitian before starting a fasting regimen.
Conclusion
Fasting is a powerful, timetested strategy for weight loss and overall health improvement. By understanding the science behind how it works and by choosing a method that fits your lifestyle, you can harness your body's innate ability to burn fat, regulate hormones, and repair itself. We believe that a fasting lifestyle, when combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise, can be a transformative experience, leading not only to a healthier weight but also to a renewed sense of energy, vitality, and wellbeing.
Comments
Post a Comment